1.
Data Warehousing Schemas
A logical representation of the
entire database is known as data warehousing schemas. A database requires
relational model but Data Warehouse (DWH) uses star schema, snowflake schema,
etc.
3.1Prerequisites for schema
Before knowing schemas
the prominent object to learn is
·
Fact
Tables
·
Dimension
Tables
Fact
Table
A fact table
is a table created to store the measurement, metrics and facts of any business
process according to business requirements. It is almost surrounded by dimension
tables. It has minimum two columns one which stores the references to the
dimension table and another one to store extra valuable data. Primary Key of
fact table are usually composite primary keys.
Steps to define Fact
Table.
Ø
Identify a business process
for analysis (like sales).
Ø
Identify measures of facts
(sales dollar), by asking questions like 'What number of XX are relevant for
the business process?', replacing the XX with various options that make sense
within the context of the business.
Ø Identify dimensions
for facts (product dimension, location dimension, time dimension, organization
dimension)
Ø
List the columns that describe
each dimension (region name, branch name, business unit name).
Ø
Determine the lowest level
(granularity) of summary in a fact table (e.g. sales dollars).
Dimension Table
It
is one of the companions to the fact table. This table is nothing but a part of
fact table which contains all the description about the business in the form
text, that is why we call it as descriptive attribute table. The goal of a dimension table is to create
standardized, conformed dimensions that can be shared across the enterprise's
data warehouse environment, and enable joining to multiple fact tables
representing various business processes.
3.2Types of Schemas
There are various types of DWH
schemas which are as follows:
·
Star
Schema
·
Snowflake
Schema
·
Fact
Constellation Schema
These all schemas mentioned above are
used day to day in data warehousing, most frequently used schema is Star
Schema.
Star Schema
The schema makes the star combination of fact table and
dimension tables. One fact table will be in centre surrounded by dimension
tables. Each dimension in a star schema is represented with only one dimension
table.
Dimension Table contains set of attributes which is nothing
but the descriptive information about business.
The above example is about sales data of company with respect
to four dimensions time, item, location and branch. The fact table also
contains the business related specific description, for example here
dollars_sold and units_sold.
Snowflake Schema
In snowflake schema, each dimension table itself acts as a
reference to another dimension table. To clear this we have an example, one
dimension table named as item has column supplier_key which in return is the
reference to the supplier dimension table.
This is required only if the tables are normalized, all the
dimension tables are to be normalized for this feature.
Due to normalization in the snowflake schema, the redundancy
is reduced and becomes easy to store and maintain the data.
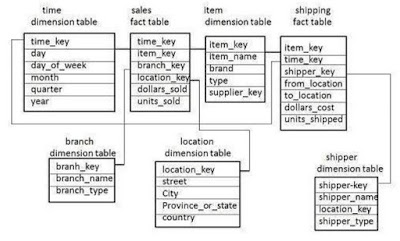
Fact Constellation Schema
The schema which has multiple fact tables is known as fact
constellation schema also known as galaxy schema. For example here we have two
fact tables sales and shipping.
Both share same dimension table items for sales and shipping
orders. It is possible to share the dimension table between fact tables.


No comments:
Post a Comment